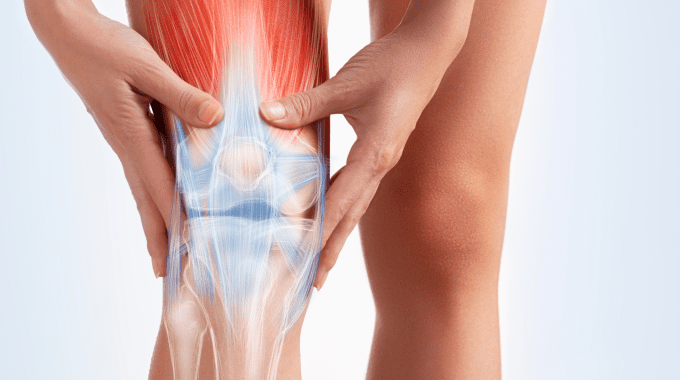
An ACL tear is a common knee injury that affects the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), a key stabilizer in the knee joint. ACL tears are often caused by sudden stops, changes in direction, or direct impact during sports. Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, and instability in the knee.
Physiotherapy plays a critical role in ACL tear recovery by managing pain, restoring knee function, and preventing further injury. The treatment plan may include strength training, range of motion exercises, and functional rehabilitation tailored to the individual's needs.
Physiotherapy for ACL tears focuses on rebuilding strength and stability in the knee. A comprehensive program helps in regaining full range of motion, improving muscle function, and addressing any compensatory movement patterns to ensure a safe return to activities.
Reduces pain and swelling
Restores knee strength and stability
Enhances range of motion and flexibility
Facilitates a safe return to sports and activities
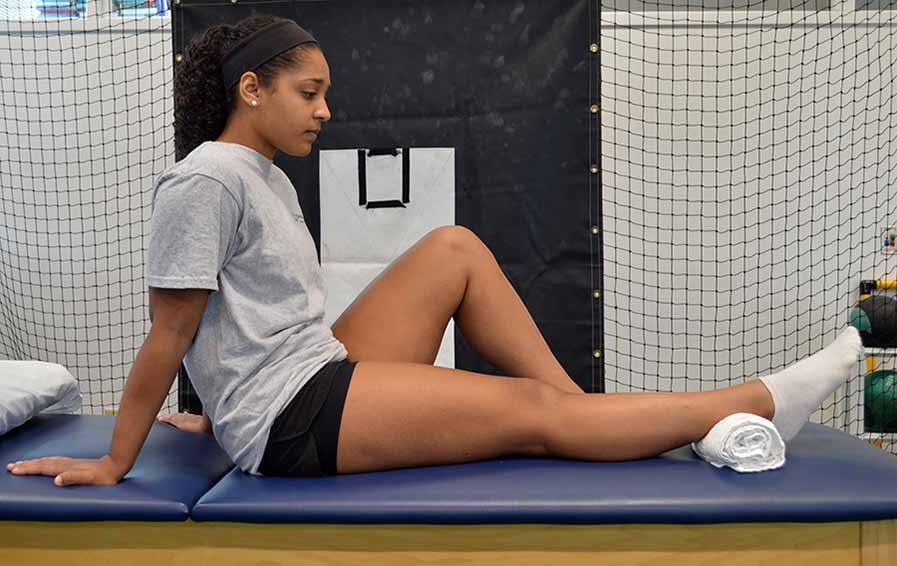

Here are some common questions we receive about ACL tears and our physiotherapy treatments:
ACL tears are commonly caused by sudden, forceful movements such as twisting or pivoting, especially during sports activities. They can also occur from direct impacts to the knee or from landing awkwardly after a jump.
Physiotherapy aids in ACL recovery by managing pain, reducing swelling, and improving knee strength and stability. Treatment typically involves a combination of exercises, manual therapy, and education to support recovery and prevent future injuries.
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the tear and the treatment approach. Generally, it can take several months of physiotherapy to regain full function and strength, with some cases requiring surgical intervention followed by extensive rehabilitation.
During physiotherapy, the therapist will assess your knee condition and develop a customized treatment plan. This may include exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion, as well as techniques to alleviate pain and facilitate functional recovery.