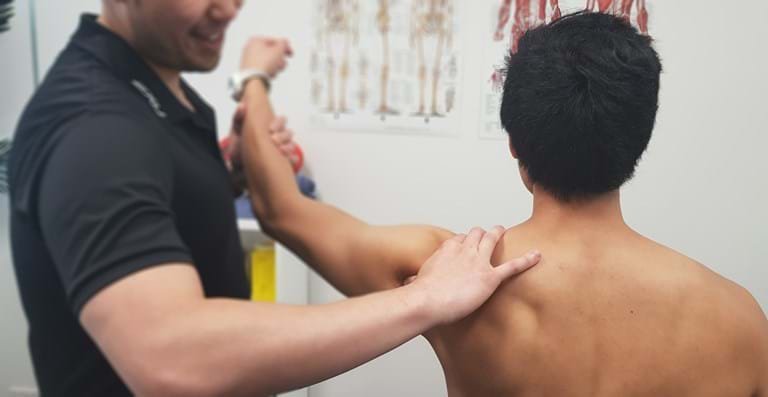
Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near joints. It commonly affects the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees. Bursitis is often caused by repetitive motion or pressure on the joint, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Physiotherapy is essential in managing bursitis by alleviating pain, reducing inflammation, and restoring movement. Treatment may include exercises to improve joint function, manual therapy, and education on joint protection to prevent further irritation.
Physiotherapy helps manage bursitis by addressing the underlying causes, such as poor posture or repetitive stress. A tailored physiotherapy program can reduce pain, enhance joint mobility, and strengthen the muscles around the affected joint, preventing future episodes.
Relieves pain and reduces inflammation
Improves joint flexibility and strength
Enhances joint stability and prevents recurrence
Speeds up recovery and reduces the need for medication

Here are some common questions we receive about bursitis and our physiotherapy treatments:
Bursitis is usually caused by repetitive stress or prolonged pressure on the joint. It can also result from injury or infections. Activities involving repetitive motions or excessive pressure on the joints can increase the risk of developing bursitis.
Physiotherapy can alleviate symptoms of bursitis by addressing the inflammation, improving joint function, and providing strategies to avoid future irritation. Treatments may include exercises, manual therapy, and advice on activity modifications.
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the bursitis and the effectiveness of the treatment plan. Many patients experience relief within a few weeks of starting physiotherapy, but full recovery may take longer.
During your physiotherapy sessions, the therapist will assess the affected joint and design a treatment plan tailored to your needs. This plan may include exercises, manual techniques, and guidance on managing activities to prevent further irritation.